sql
来自《数据库系统概论(第6版)》第三章
基于Oracle 19数据库
SQL
模式的定义与删除
在数据库中,一个模式下通常包括多个表、视图和索引等数据库对象。一个数据库中可以建立多个模式。
在Oracle数据库中,模式的概念即用户。
创建模式:
1 | create user c##atri identified by xxxxxxxxx; |
需在用户名前添加前缀C##
切换模式:
1 | alter session set current_schema = c##atri; |
删除模式:
1 | DROP USER username CASCADE; |
模式下包含的东西也被删除了。
基本表的建立
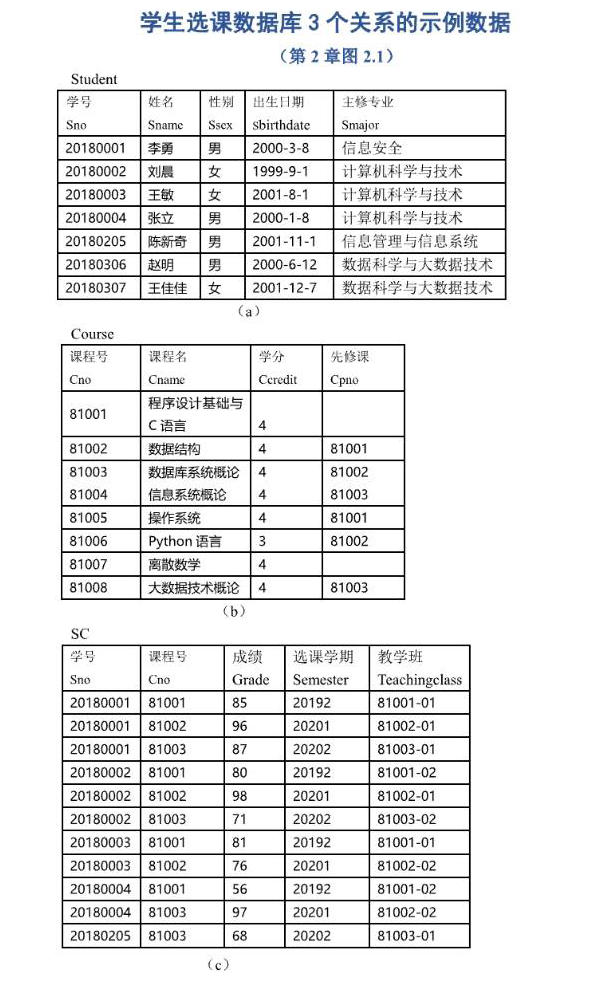
为了方便后续重点语句的展示,我这里按照书上的二维码,准备几个表。
sc.sql:
1 | DROP TABLE SC; |
表长这样:
关于修改表、删除表什么的,这里就摆了hh
索引的建立与删除
也摆了,Coming soon(???)
数据查询
单表查询
例子学习法,学习之前请先导入上面的sql文件
重点
(1)查询指定列
查询全体学生的学号与姓名
1 | select sno, sname |
(2)查询全部列
查询全体学生的详细记录
1 | select * from student; |
(3)查询经过计算的值
select子句的目标列表达式可以是算术表达式、字符串常量、函数等
查询全体学生的年龄
1 | select sname, (extract(year from current_date) - extract(year from sbirthdate)) "年龄" |
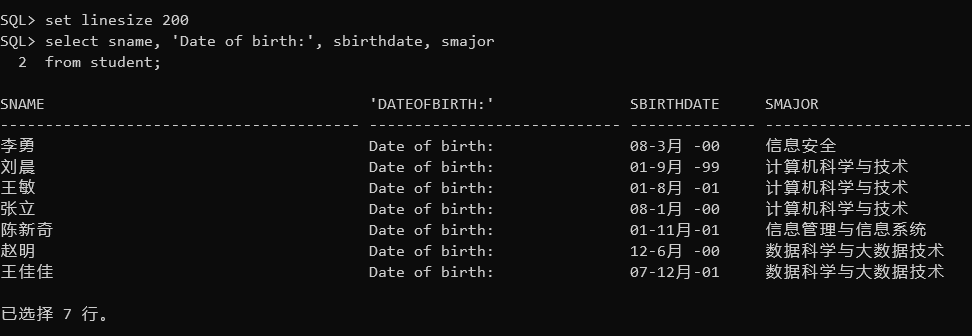
查询全体学生的姓名、出生日期和主修专业
1 | select sname, 'Date of birth:', sbirthdate, smajor |
(4)消除取值重复的行
查询选修了课程的学生学号
1 | select distinct sno from sc; |
(5)查询满足条件的元组
比较:=,>,<,.>=,<=,!=,<>,!>,!<,NOT+
查询主修计算机科学与技术专业全体学生的姓名
1 | select sname |
查询所有2000年后(包括2000年)出生的学生姓名及其性别
1 | select sname, ssex |
查询考试成绩不及格的学生的学号
1 | select distinct sno |
确定范围:(not) between ... and ...
查询年龄在20~23岁(包括20岁和23岁)之间的学生的学生的姓名、出生年月和主修专业
1 | select sname, sbirthdate, smajor |
查询年龄不在20~23岁(包括20岁和23岁)之间的学生的学生的姓名、出生年月和主修专业
1 | select sname, sbirthdate, smajor |
确定集合
谓词:in <值表>, not in <值表>
查询计算机科学与技术专业和信息安全专业学生的姓名和性别
1 | select sname, ssex |
字符匹配
[not] like '<匹配串>' [escape '<换码字符>']
%:任意长度(可以为0)的字符串
_:任意单个字符
查询学号为20180003的学生的详细情况
1 | select * |
查询所有姓刘学生的姓名、学号和性别
1 | select sname, sno, ssex |
查询2018级学生的学号和姓名
1 | select sno, sname |
查询课程号为81开头,最后一位是6的课程名称和课程号
1 | select cname, cno |
查询DB_Design课程的课程号和学分
1 | select cno, ccredit |
涉及空值的查询:is [not] NULL
is 不能用 = 代替
某些学生选修课程后没有参加考试,有选课记录,但没有考试成绩。查询缺少成绩的学生的学号和相应的课程号。
1 | select sno, cno |
多重条件查询:and or,and优先级高于or
查询主修计算机科学与技术专业2000年(包括2000年)以后出生的学生学号、姓名和性别。
1 | select sno, sname, ssex |
order by: 按一个或多个属性值升序(降序)排列,对于空值的实现依具体系统实现决定
查询选修了81003号课程的学生的学号及其成绩,查询结果按分数的降序排列
1 | select sno, grade |
查询全体学生选修课程情况,查询结果先按照课程号升序排列,同一课程中按成绩降序排列。
1 | select * from sc |
聚集函数
统计元组个数:count(*)
统计一列中值的个数:count([distinct|all] 列名)
计算一列值的总和(此列必须为数值型):sum([distinct|all] 列名)
计算一列值的平均值(此列必须为数值型):avg([distinct|all] 列名)
求一列中的最大值和最小值:max/min([distinct|all] 列名)
查询选修了课程的学生人数
1 | select count(distinct sno) |
计算选修81001号课程的学生平均成绩
1 | select avg(grade) |
查询选修1号课程的学生最高分数
1 | select max(grade) |
查询学号为20180003学生选修课程的总学分数
1 | select sum(ccredit) |
group by子句分组:
- 按指定的一列或多列值分组,值相等的为一组
- 如果未对查询结果分组,聚集函数将作用于整个查询结果
- 分组后,聚集函数将作用于每一个组
求各个课程号及选修该课程的人数
1 | select cno, count(sno) |
查询2019年第2学期选修了10门以上课程的学生学号
1 | select sno |
having 和 where 的区别:
- where子句作用于基表或视图,从中选择满足条件的元组
- having短语作用于组,从中选择满足条件的组
limit:限制元组数量
查询选修了数据库系统概论课程的成绩排名前10名的学生学号
1 | select sno |
limit关键字在oracle数据库是不支持的,需要用rownum来实现相同功能:
1 | select * |
连接查询
即同时涉及两个以上的表的查询
(1)等值与非等值连接查询
查询每个学生及其选修课程的情况
1 | select student.*, sc.* |
(2)自然连接查询
查询每个学生的学号、姓名、性别、出生日期、主修专业及该学生选修课程的课程号与成绩
1 | select student.sno, sname, ssex, sbirthdate, smajor, cno, grade |
(3)复合条件连接查询
在连接谓词的基础上增加选择谓词,组成复合条件
查询选修81002号课程且成绩在90分以上的所有学生的学号和姓名
1 | select student.sno, sname |
(4)自身连接查询
查询每一门课的间接先修课(即先修课的先修课)
1 | select first.cno, second.cpno |
(5)外连接查询
外连接操作以指定表为连接主体,将主体表中不满足连接条件的元组一并输出。
以Student表为主体列出每个学生的基本情况及其选课情况,若某个学生没有选课,则只输出其基本情况的数据,而把选课信息填为空值NULL
1 | select student.sno, sname, ssex, sbirthdate, smajor, cno, grade |
(6)多表连接查询
两个以上的表的连接。
嵌套查询
一个select-from-where语句称为一个查询块
将一个查询块嵌套到另一个查询块的where子句或having短语的条件中的查询称为嵌套查询
不相关子查询
子查询的查询条件不依赖于父查询,可以由里向外逐层处理。
- 相关子查询
首先取外层查询表的第一个元组,根据它与内层查询相关的属性值处理内层查询,若where返回真,则加入结果表。然后重复这一过程。
(1)IN谓词
查询与“刘晨”在同一个主修专业的学生学号、姓名和主修专业
1 | select sno, sname, smajor |
查询选修了课程名为“信息系统概论”的学生的学号和姓名
1 | select sno, sname |
(2)带有比较运算符的子查询
当能确切知道内层查询返回单值时,可用比较运算符。
找出每个学生超过他选修课程平均成绩的课程号
1 | select sno, cno |
先从外层的元组中取出x.sno,然后再内层中寻找y.sno=x.sno的元组,求avg(grade),用该值代替内层查询,重新得到外层查询。
(3)带有ANY(SOME)或ALL谓词
必须同时使用比较运算符
查询非计算机科学技术专业中比计算机科学技术专业任意一个学生年龄小(出生日期晚)的学生的姓名、出生日期和主修专业
1 | select sname, sbirthdate, smajor |
可以和一些聚集函数进行等价转换。

(4)EXISTS谓词
带有EXISTS谓词的子查询只产生逻辑真值 true 或
false ,取决于内层查询是否非空。
查询没有选修81001号课程的学生姓名
1 | select sname |
可用 exists/not exists 实现全称量词(难点):
1 | select sname |
转换,不存在没有被该学生选修的课程,双重否定。
可用exists/not exists实现逻辑蕴涵(难点)
用逻辑蕴含来表达:查询学号为x的学生,对所有的课程y,只要20180002号学生选修了课程y,那么x也选修了y。
用p表示谓词“学生20180002选修了课程y”
用q表示谓词“学生x选修了课程y”
则上述查询为
. 可等价转换为
. 语义为:不存在(第一个not exists)这样的课程y,它即被20180002选修,但不被(第二个not exists)x选修。
1 | select sno |
其实我也不是很理解,这真的很抽象。
集合查询
UNION、INTERSECT、EXCEPT
查询计算机科学与技术专业的学生及年龄不大于19岁(包括等于19岁)的学生
1 | select * from student where smajor = '计算机科学与技术' |
查询计算机科学与技术专业的学生与年龄不大于19岁的学生的交集
1 | select * from student where smajor = '计算机科学与技术' |
基于派生表的查询
子查询不止可以出现在where子句中,还可以出现在from子句中。
找出每个学生超过他自己选修课程平均成绩的课程号
1 | select sno, cno |
数据更新
sql语言练习
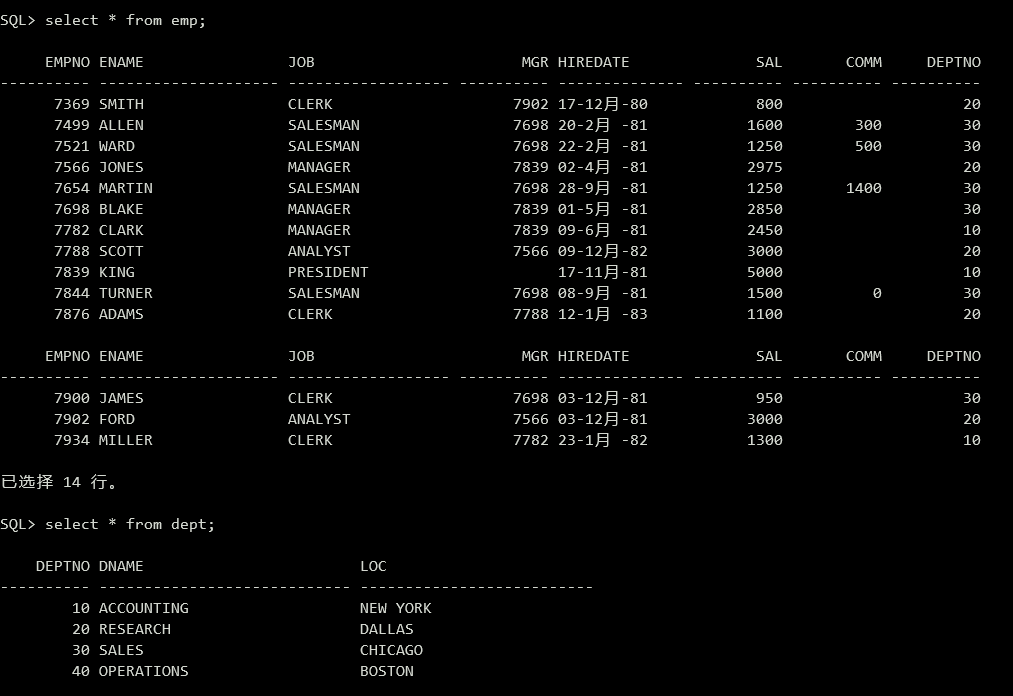
首先运行该 emp.sql 文件:
1 | //在SQL*PLUS里用@命令执行 |
(1)在emp表上添加如下约束:入职时间不得晚于2021年7月8日,工资不能为负值,deptno为emp的外码。
1 | alter table emp add constraint hiredate_chk check(hiredate <= DATE '2021-07-08'); |
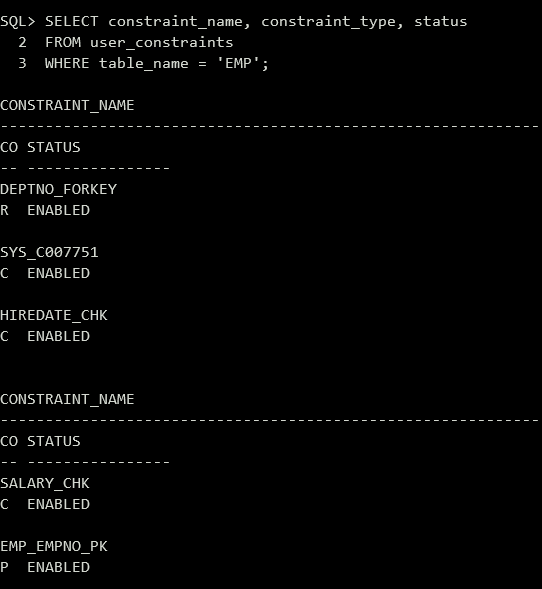
查询数据字典,可查看EMP表(需大写)所有约束。
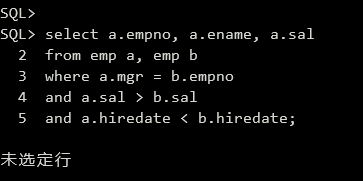
(2)查询比他/她的经理工资高且雇佣时间长的雇员的雇员号、雇员名以及工资。
1 | select a.empno, a.ename, a.sal |
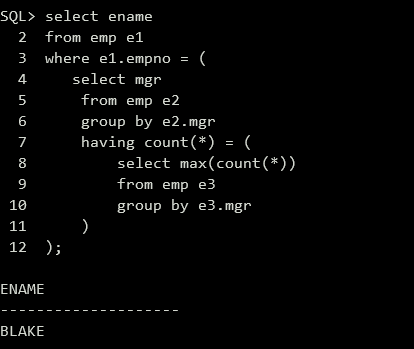
(3)查询雇佣人数最多的经理名。
1 | select ename |
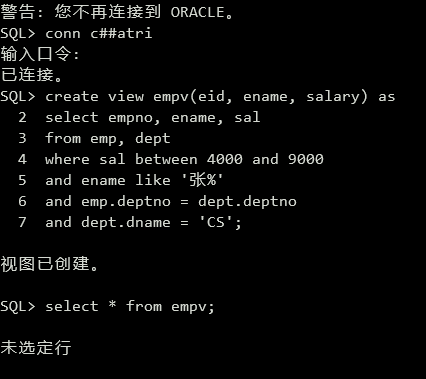
(4)创建CS部门工资在4000~9000元间的姓“张”的雇员视图empv(eid, ename, salary)。
1 | create view empv(eid, ename, salary) as |
(5)查询所有部门没有雇员的工资大于3000元的部门名。
1 | select dname |
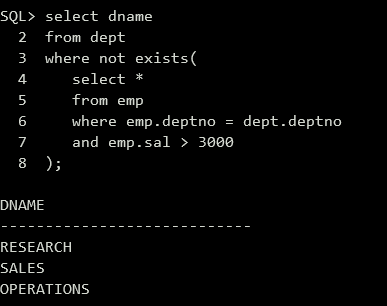
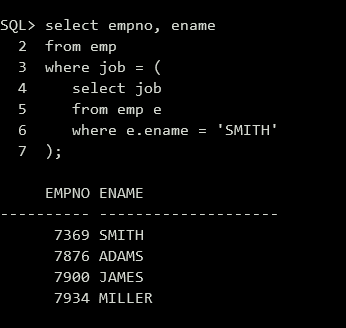
(6)查询与雇员“SMITH”同一职业的雇员号和雇员名。
1 | select empno, ename |
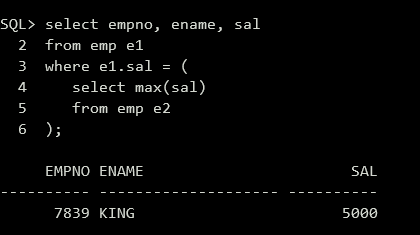
(7)查询雇员工资最高的雇员号、雇员名和工资。
1 | select empno, ename, sal |
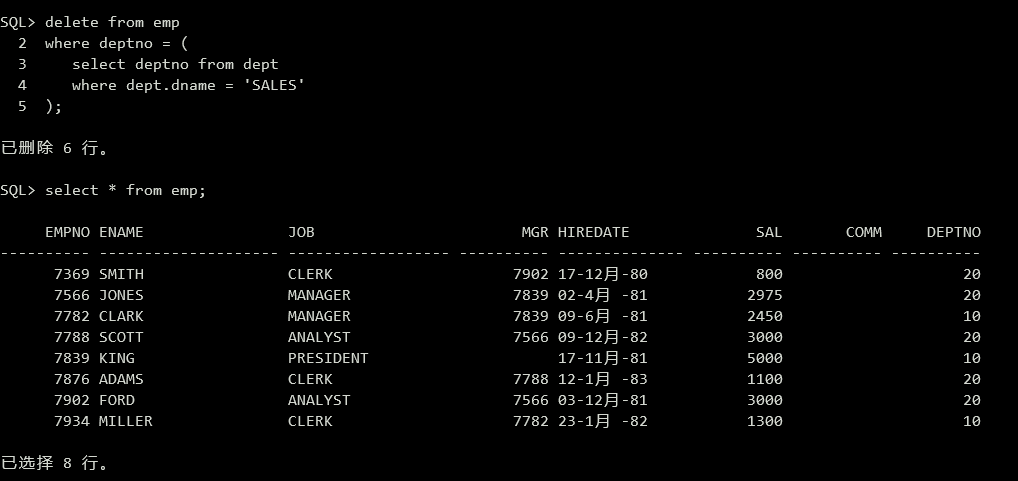
(8)删除“sales"部门的雇员信息。
1 | delete from emp |
(9)修改7782号雇员的职业和部门号与7788号雇员相同。
1 | update emp |
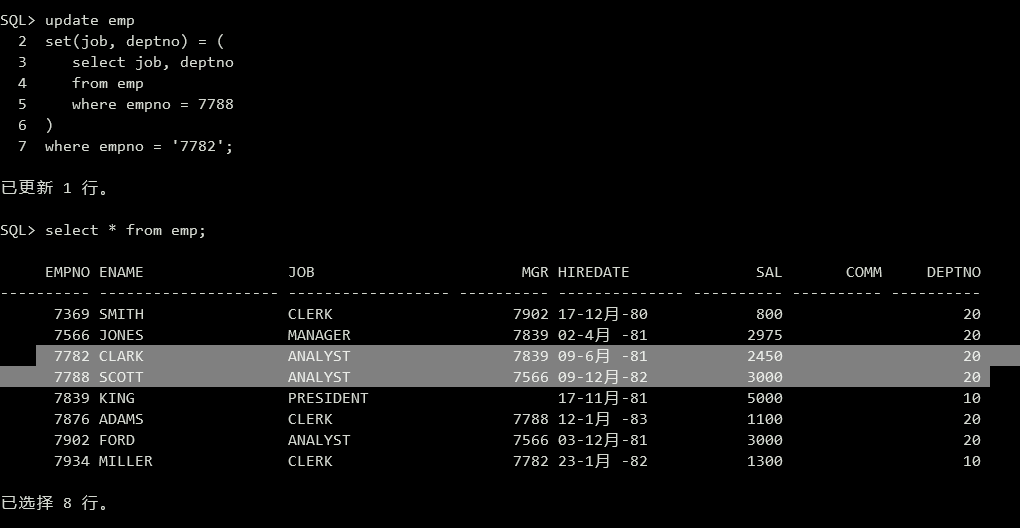
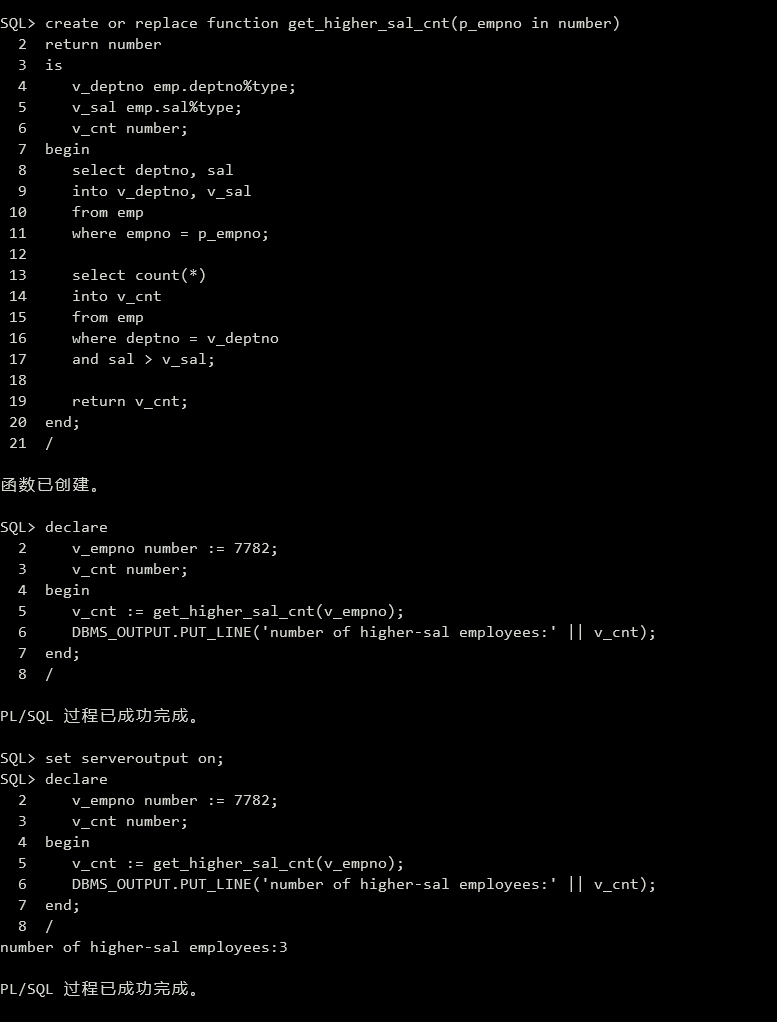
(10)创建一个函数,给定一个雇员号,返回该雇员所在部门比他/她工资高的雇员数目。
1 | create or replace function get_higher_sal_cnt(p_empno in number) |
调用函数:
1 | declare |